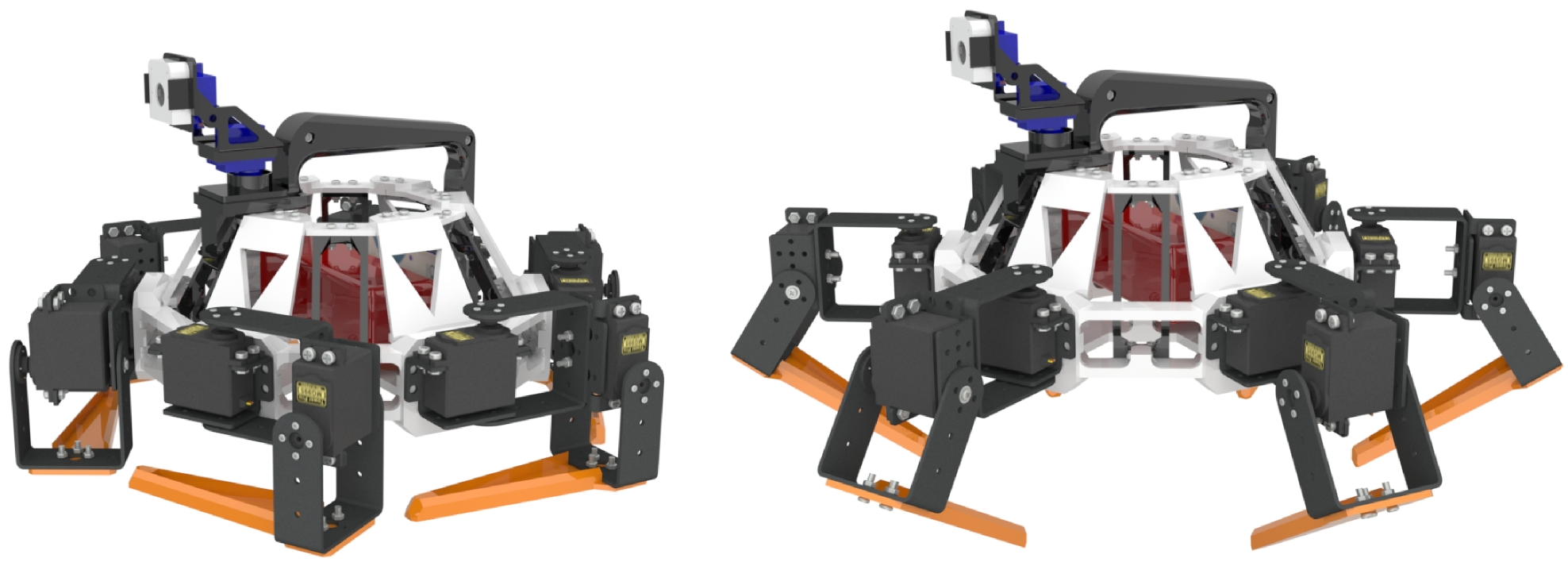
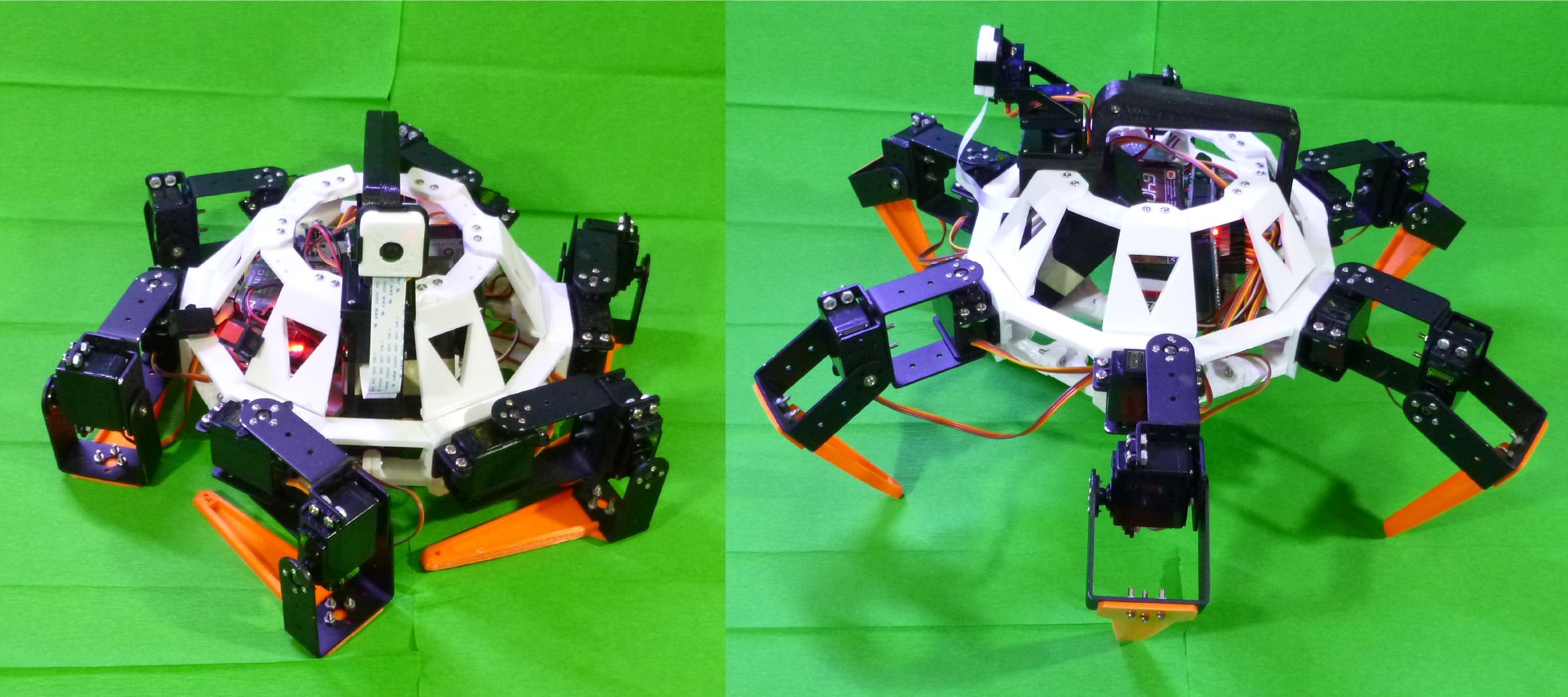
In this version (V-0.1) the robot is able to perform basic operations such as standing, and walking; the control set is command through SSH connection with a feedback video feed form the Raspberry Pi camera module. Basic sequences for walking and turning are implemented deep in to the Arduino microcontroller to simplify communication between the Raspberry Pi board and the rest of the hardware.
Some detail in the design, construction and configurin of the robot are formally aviable here:
Pi: Configuring SSH, VNC and Camera Module Streaming – See more at:
https://www.libremechanics.com/#sthash.fkVVhLpY.dpuf
Pi: Configuring SSH, VNC and Camera Module Streaming – See more at:
https://www.libremechanics.com/#sthash.fkVVhLpY.dpuf
Pi: Configuring SSH, VNC and Camera Module Streaming – See more at:
https://www.libremechanics.com/#sthash.fkVVhLpY.dpuf
- Designs: Repositories / Thingiverse for 3D print.
- Code: Repositories-
Main characteristics:
- Modular 3D printed design for impact resistance and durability.
- Model available as Open-Hardware.
- 2 DOF using common high torque RC servos.
- 2 DOF camera head.
- Hand grip for fast deploy.
- Controlled by Raspberry Pi board and Arduino Mega microcontroller.
- Powered by lithium polymer battery, totally independent and wireless.
- RC and Wi-Fi connection.
- Real time video feed using Raspberry Pi camera module.
- Multiple movements such as resting, standing, leaning, and walking.
Video:
About the structure:
The robot structure is made of 3D printed PLA and ABS on particular printing pattern and orientations ensuring maximum resistance to vibrations, falls, obstacle hits and external forces. The maximum drops test performed was made at a high of 1.5 m with the legs in standing position.
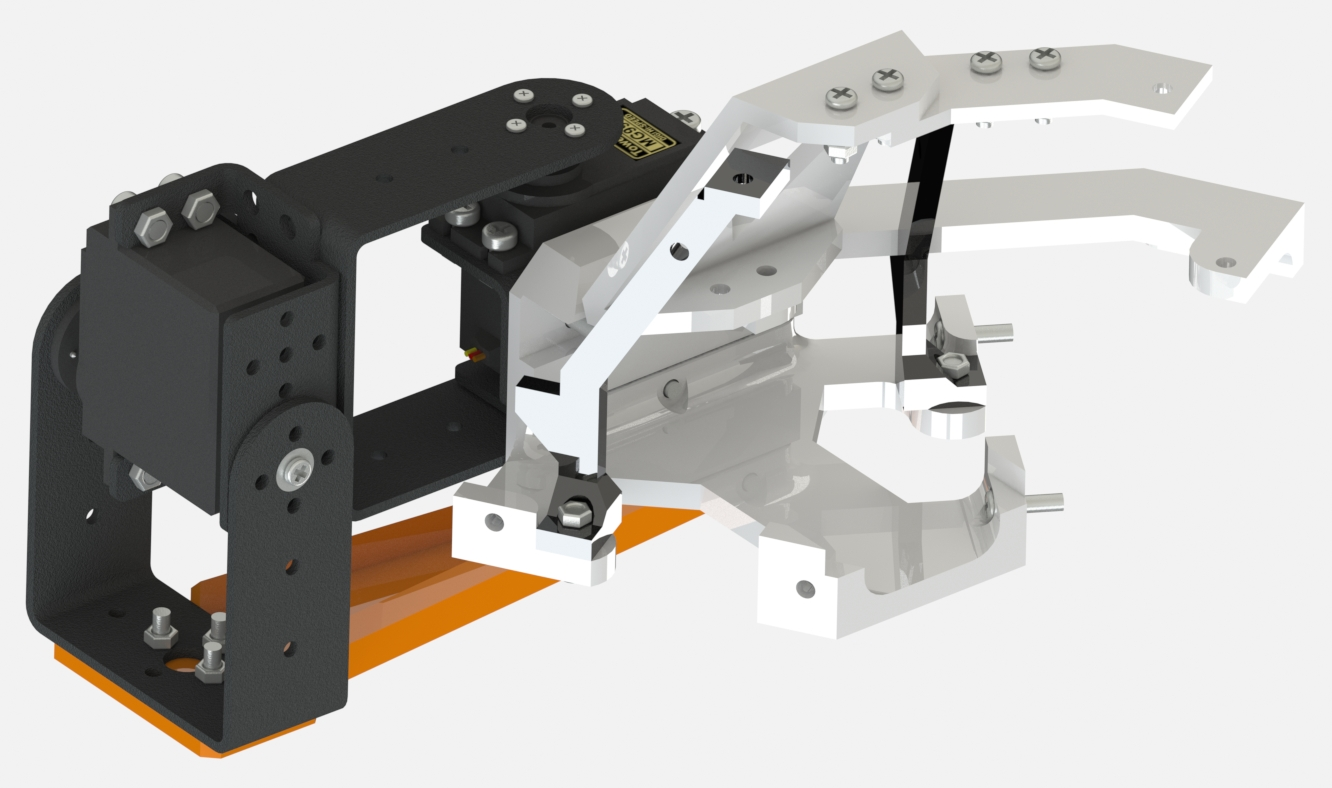
Each leg module contains 1/6 of the total body assembly and its parts are connected using standard sujections parts as 3M screws and bolts.
The hand grip assembly allows the user to grab, transport and deploy the robot easily.

About the power supply:

A lithium
polymer battery is used to power both the power circuit (servos) and the
control boards, special UBEC regulators are use to ensure 5.0V and 6.0V
to each circuit; and a voltage monitor nostanly checks the battery
state. Although the consumption exceeds 6000mAh or even 8000mAh, the
Li-Po battery shows no lack of capacity even on long periods of testing.
The battery capacity exceeds the “forbearance” of the user on field
test of more than 6 hours. No actual maximum time of operation has been
recorded. It is estimated for this feature to change when additional
actuators are installed.
Future versions capabilities:
- 18 DOF structure, 3 ODV per leg
- Force sensor on each leg
- Inertial measurement unit for “reflex functions” implementation.
- Microphone and speakers.
- Flashlight and UV blacklight.
- Rugged waterproof suit.
 Libre Mechanics it’s an Open Knowledge project created to offer a useful platform of information related with the development and research of Mechanical Engineering themes and similar fields, higly related with the use of Open Source and Software Libre tools. Here you will find a wide variety of projects, publications and scientific material available as references for developing their own projects, also guides and tutorials that allow you to take advantage of free software tools available today.
Libre Mechanics it’s an Open Knowledge project created to offer a useful platform of information related with the development and research of Mechanical Engineering themes and similar fields, higly related with the use of Open Source and Software Libre tools. Here you will find a wide variety of projects, publications and scientific material available as references for developing their own projects, also guides and tutorials that allow you to take advantage of free software tools available today.